获取给定当前点、距离和方位的纬度/经度
- 2025-03-04 08:27:00
- admin 原创
- 97
问题描述:
给定一个现有的纬度/经度点、距离(以公里为单位)和方位(以度为单位转换为弧度),我想计算新的纬度/经度。这个网站反复出现,但我就是无法让公式对我有用。
上述链接中的公式如下:
lat2 = asin(sin(lat1)*cos(d/R) + cos(lat1)*sin(d/R)*cos(θ))
lon2 = lon1 + atan2(sin(θ)*sin(d/R)*cos(lat1), cos(d/R)−sin(lat1)*sin(lat2))
上述公式适用于 MSExcel,其中:
asin = arc sin()
d = distance (in any unit)
R = Radius of the earth (in the same unit as above)
and hence d/r = is the angular distance (in radians)
atan2(a,b) = arc tan(b/a)
θ is the bearing (in radians, clockwise from north);
这是我在 Python 中得到的代码。
import math
R = 6378.1 #Radius of the Earth
brng = 1.57 #Bearing is 90 degrees converted to radians.
d = 15 #Distance in km
#lat2 52.20444 - the lat result I'm hoping for
#lon2 0.36056 - the long result I'm hoping for.
lat1 = 52.20472 * (math.pi * 180) #Current lat point converted to radians
lon1 = 0.14056 * (math.pi * 180) #Current long point converted to radians
lat2 = math.asin( math.sin(lat1)*math.cos(d/R) +
math.cos(lat1)*math.sin(d/R)*math.cos(brng))
lon2 = lon1 + math.atan2(math.sin(brng)*math.sin(d/R)*math.cos(lat1),
math.cos(d/R)-math.sin(lat1)*math.sin(lat2))
print(lat2)
print(lon2)
我明白了
lat2 = 0.472492248844
lon2 = 79.4821662373
解决方案 1:
需要将答案从弧度转换回度数。有效代码如下:
from math import asin, atan2, cos, degrees, radians, sin
def get_point_at_distance(lat1, lon1, d, bearing, R=6371):
"""
lat: initial latitude, in degrees
lon: initial longitude, in degrees
d: target distance from initial
bearing: (true) heading in degrees
R: optional radius of sphere, defaults to mean radius of earth
Returns new lat/lon coordinate {d}km from initial, in degrees
"""
lat1 = radians(lat1)
lon1 = radians(lon1)
a = radians(bearing)
lat2 = asin(sin(lat1) * cos(d/R) + cos(lat1) * sin(d/R) * cos(a))
lon2 = lon1 + atan2(
sin(a) * sin(d/R) * cos(lat1),
cos(d/R) - sin(lat1) * sin(lat2)
)
return (degrees(lat2), degrees(lon2),)
lat = 52.20472
lon = 0.14056
distance = 15
bearing = 90
lat2, lon2 = get_point_at_distance(lat, lon, distance, bearing)
# lat2 52.20444 - the lat result I'm hoping for
# lon2 0.36056 - the long result I'm hoping for.
print(lat2, lon2)
# prints "52.20451523755824 0.36067845713550956"
解决方案 2:
geopy库支持这一点:
import geopy
from geopy.distance import VincentyDistance
# given: lat1, lon1, b = bearing in degrees, d = distance in kilometers
origin = geopy.Point(lat1, lon1)
destination = VincentyDistance(kilometers=d).destination(origin, b)
lat2, lon2 = destination.latitude, destination.longitude
通过https://stackoverflow.com/a/4531227/37610找到
解决方案 3:
这个问题被称为大地测量学研究中的直接问题。
这确实是一个非常常见的问题,也是经常引起困惑的问题。原因是大多数人都在寻找一个简单而直接的答案。但没有答案,因为大多数问这个问题的人没有提供足够的信息,只是因为他们没有意识到:
地球并不是一个完美的球体,因为它被两极压扁/压缩
由于(1)地球没有恒定的半径,
R请参见此处。地球并不是完全平坦的(海拔变化)等等。
由于板块运动,地理点的纬度/经度位置每年可能会发生几毫米(至少)的变化。
因此,各种几何模型使用了许多不同的假设,根据您所需的精度,这些假设的适用性也不同。因此,要回答这个问题,您需要考虑您希望结果达到什么精度。
一些例子:
我只是在寻找N|S之间较小距离( < 100公里)的最近几公里的近似位置。(地球是~平坦模型。)
latitudes`0-70 deg`我想要一个适合全球任何地方的答案,但精度只能达到几米
我想要一个超精确的定位,有效范围达到原子尺度
nanometers[nm]。我想要的答案是能够快速且容易计算并且不需要大量计算。
因此,您可以选择多种算法。此外,每种编程语言都有自己的实现或“包”,乘以模型数量和模型开发人员的特定需求。出于所有实际目的,忽略任何其他语言都是值得的javascript,因为它本质上非常类似于伪代码。因此,只需进行最少的更改,它就可以轻松转换为任何其他语言。
那么主要的模型有:
Euclidian/Flat earth model:适用于 10 公里以内的极短距离Spherical model:适用于经度距离较大,纬度差异较小的情况。热门型号:
+ 半正矢: [km] 尺度上的**米级**精度,非常简单的代码。Ellipsoidal models:在任何纬度/经度和距离上都是最准确的,但仍然是数值近似值,取决于您需要的精度。一些流行的模型是:
+ 兰伯特:数千*公里范围内精度约为***10 米**。
+ Paul D.Thomas:安多耶-兰伯特近似
+ Vincenty:**毫米级**精度和计算效率
+ Kerney :**纳米**精度
参考:
解决方案 4:
回答可能有点晚了,但在测试了其他答案后,似乎它们无法正常工作。这是我们用于系统的 PHP 代码。全方位工作。
PHP代码:
lat1 = 起点纬度(以度为单位)
long1 = 起点经度(度)
d = 距离(公里)
角度 = 方位角(度)
function get_gps_distance($lat1,$long1,$d,$angle)
{
# Earth Radious in KM
$R = 6378.14;
# Degree to Radian
$latitude1 = $lat1 * (M_PI/180);
$longitude1 = $long1 * (M_PI/180);
$brng = $angle * (M_PI/180);
$latitude2 = asin(sin($latitude1)*cos($d/$R) + cos($latitude1)*sin($d/$R)*cos($brng));
$longitude2 = $longitude1 + atan2(sin($brng)*sin($d/$R)*cos($latitude1),cos($d/$R)-sin($latitude1)*sin($latitude2));
# back to degrees
$latitude2 = $latitude2 * (180/M_PI);
$longitude2 = $longitude2 * (180/M_PI);
# 6 decimal for Leaflet and other system compatibility
$lat2 = round ($latitude2,6);
$long2 = round ($longitude2,6);
// Push in array and get back
$tab[0] = $lat2;
$tab[1] = $long2;
return $tab;
}
解决方案 5:
我将 Brad 的回答移植到了 vanilla JS 答案中,不再依赖 Bing 地图
https://jsfiddle.net/kodisha/8a3hcjtd/
// ----------------------------------------
// Calculate new Lat/Lng from original points
// on a distance and bearing (angle)
// ----------------------------------------
let llFromDistance = function(latitude, longitude, distance, bearing) {
// taken from: https://stackoverflow.com/a/46410871/13549
// distance in KM, bearing in degrees
const R = 6378.1; // Radius of the Earth
const brng = bearing * Math.PI / 180; // Convert bearing to radian
let lat = latitude * Math.PI / 180; // Current coords to radians
let lon = longitude * Math.PI / 180;
// Do the math magic
lat = Math.asin(Math.sin(lat) * Math.cos(distance / R) + Math.cos(lat) * Math.sin(distance / R) * Math.cos(brng));
lon += Math.atan2(Math.sin(brng) * Math.sin(distance / R) * Math.cos(lat), Math.cos(distance / R) - Math.sin(lat) * Math.sin(lat));
// Coords back to degrees and return
return [(lat * 180 / Math.PI), (lon * 180 / Math.PI)];
}
let pointsOnMapCircle = function(latitude, longitude, distance, numPoints) {
const points = [];
for (let i = 0; i <= numPoints - 1; i++) {
const bearing = Math.round((360 / numPoints) * i);
console.log(bearing, i);
const newPoints = llFromDistance(latitude, longitude, distance, bearing);
points.push(newPoints);
}
return points;
}
const points = pointsOnMapCircle(41.890242042122836, 12.492358982563019, 0.2, 8);
let geoJSON = {
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": []
};
points.forEach((p) => {
geoJSON.features.push({
"type": "Feature",
"properties": {},
"geometry": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [
p[1],
p[0]
]
}
});
});
document.getElementById('res').innerHTML = JSON.stringify(geoJSON, true, 2);
此外,我添加了geoJSON导出功能,因此您只需将生成的 geoJSON 粘贴到:http://geojson.io/#map=17/41.89017/12.49171即可立即查看结果。
结果: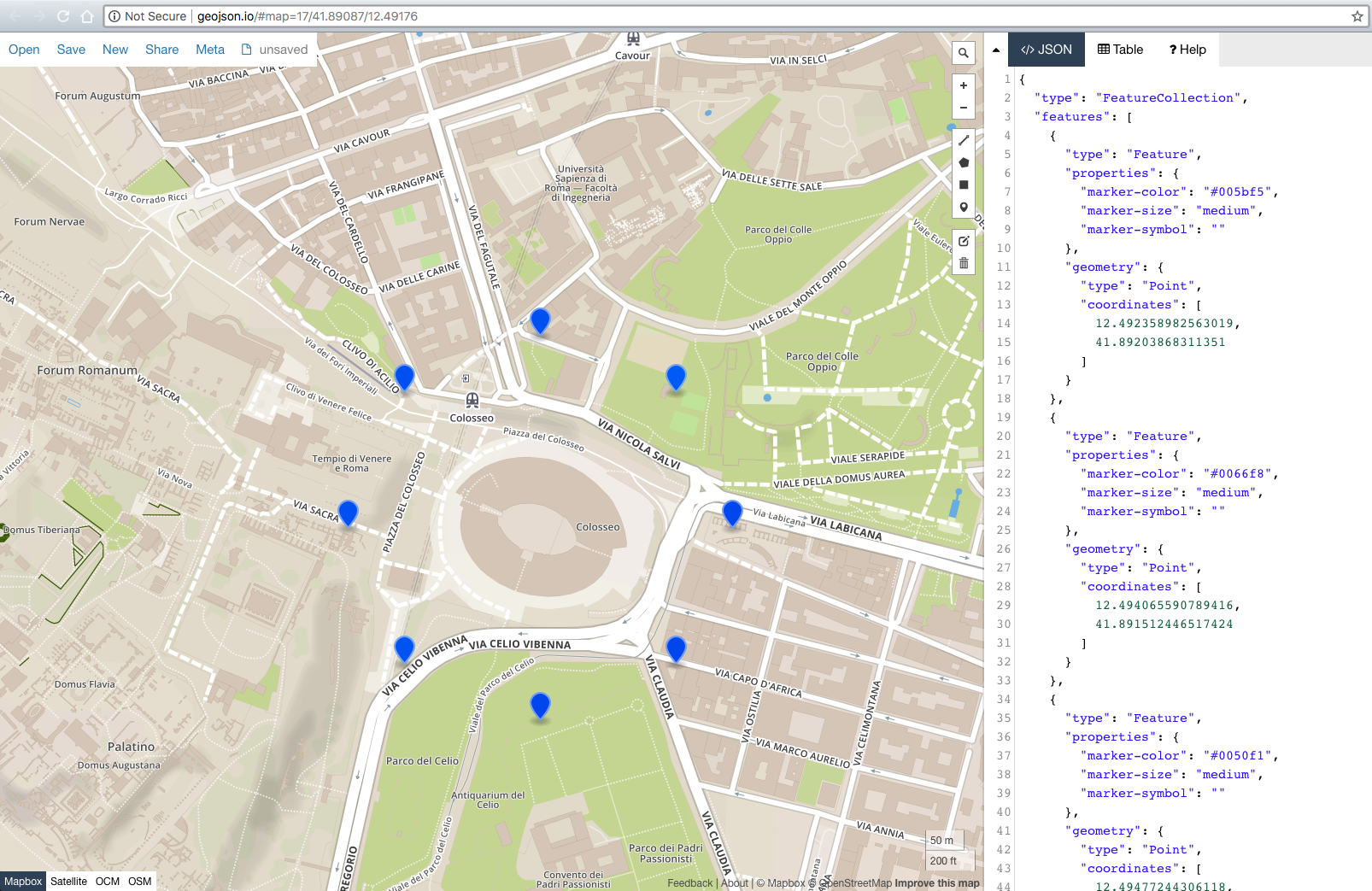
解决方案 6:
使用 geopy 的快捷方法
from geopy import distance
#distance.distance(unit=15).destination((lat,lon),bering)
#Exemples
distance.distance(nautical=15).destination((-24,-42),90)
distance.distance(miles=15).destination((-24,-42),90)
distance.distance(kilometers=15).destination((-24,-42),90)
解决方案 7:
lon1 和 lat1 以度为单位
brng = 方位角(以弧度为单位)
d = 距离(公里)
R = 地球半径(以公里为单位)
lat2 = math.degrees((d/R) * math.cos(brng)) + lat1
long2 = math.degrees((d/(R*math.sin(math.radians(lat2)))) * math.sin(brng)) + long1
我在 PHP 中实现了您的算法和我的算法,并对其进行了基准测试。此版本的运行时间约为 50%。生成的结果相同,因此从数学上看似乎是等价的。
我没有测试上面的 python 代码,所以可能存在语法错误。
解决方案 8:
我将 Python 移植到了 Javascript。这将返回一个 Bing MapsLocation对象,您可以随意更改。
getLocationXDistanceFromLocation: function(latitude, longitude, distance, bearing) {
// distance in KM, bearing in degrees
var R = 6378.1, // Radius of the Earth
brng = Math.radians(bearing) // Convert bearing to radian
lat = Math.radians(latitude), // Current coords to radians
lon = Math.radians(longitude);
// Do the math magic
lat = Math.asin(Math.sin(lat) * Math.cos(distance / R) + Math.cos(lat) * Math.sin(distance / R) * Math.cos(brng));
lon += Math.atan2(Math.sin(brng) * Math.sin(distance / R) * Math.cos(lat), Math.cos(distance/R)-Math.sin(lat)*Math.sin(lat));
// Coords back to degrees and return
return new Microsoft.Maps.Location(Math.degrees(lat), Math.degrees(lon));
},
解决方案 9:
感谢@kodisha,这是一个 Swift 版本,但对地球半径的计算进行了改进,并且更加精确:
extension CLLocationCoordinate2D {
func earthRadius() -> CLLocationDistance {
let earthRadiusInMetersAtSeaLevel = 6378137.0
let earthRadiusInMetersAtPole = 6356752.314
let r1 = earthRadiusInMetersAtSeaLevel
let r2 = earthRadiusInMetersAtPole
let beta = latitude
let earthRadiuseAtGivenLatitude = (
( pow(pow(r1, 2) * cos(beta), 2) + pow(pow(r2, 2) * sin(beta), 2) ) /
( pow(r1 * cos(beta), 2) + pow(r2 * sin(beta), 2) )
)
.squareRoot()
return earthRadiuseAtGivenLatitude
}
func locationByAdding(
distance: CLLocationDistance,
bearing: CLLocationDegrees
) -> CLLocationCoordinate2D {
let latitude = self.latitude
let longitude = self.longitude
let earthRadiusInMeters = self.earthRadius()
let brng = bearing.degreesToRadians
var lat = latitude.degreesToRadians
var lon = longitude.degreesToRadians
lat = asin(
sin(lat) * cos(distance / earthRadiusInMeters) +
cos(lat) * sin(distance / earthRadiusInMeters) * cos(brng)
)
lon += atan2(
sin(brng) * sin(distance / earthRadiusInMeters) * cos(lat),
cos(distance / earthRadiusInMeters) - sin(lat) * sin(lat)
)
let newCoordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2D(
latitude: lat.radiansToDegrees,
longitude: lon.radiansToDegrees
)
return newCoordinate
}
}
extension FloatingPoint {
var degreesToRadians: Self { self * .pi / 180 }
var radiansToDegrees: Self { self * 180 / .pi }
}
解决方案 10:
虽然也有些晚了,但对于那些可能发现这一点的人来说,使用geographiclib库将获得更准确的结果。查看测地线问题描述和 JavaScript 示例,以轻松介绍如何使用它来回答主题问题以及许多其他问题。以多种语言实现,包括 Python。如果您关心准确性,这比自己编写代码要好得多;比早先“使用库”建议中的 VincentyDistance 更好。正如文档所述:“重点是返回准确结果,误差接近舍入(约 5-15 纳米)。”
解决方案 11:
只需交换 atan2(y,x) 函数中的值即可。不是 atan2(x,y)!
解决方案 12:
如果有人想要这个,我将@David M 的答案移植到了 java...我确实得到了略有不同的结果 52.20462299620793, 0.360433887489931
double R = 6378.1; //Radius of the Earth
double brng = 1.57; //Bearing is 90 degrees converted to radians.
double d = 15; //Distance in km
double lat2 = 52.20444; // - the lat result I'm hoping for
double lon2 = 0.36056; // - the long result I'm hoping for.
double lat1 = Math.toRadians(52.20472); //Current lat point converted to radians
double lon1 = Math.toRadians(0.14056); //Current long point converted to radians
lat2 = Math.asin( Math.sin(lat1)*Math.cos(d/R) +
Math.cos(lat1)*Math.sin(d/R)*Math.cos(brng));
lon2 = lon1 + Math.atan2(Math.sin(brng)*Math.sin(d/R)*Math.cos(lat1),
Math.cos(d/R)-Math.sin(lat1)*Math.sin(lat2));
lat2 = Math.toDegrees(lat2);
lon2 = Math.toDegrees(lon2);
System.out.println(lat2 + ", " + lon2);
解决方案 13:
这是基于 Ed Williams Aviation Formulary 的 PHP 版本。PHP 中模数的处理方式略有不同。这对我来说很管用。
function get_new_waypoint ( $lat, $lon, $radial, $magvar, $range )
{
// $range in nm.
// $radial is heading to or bearing from
// $magvar for local area.
$range = $range * pi() /(180*60);
$radial = $radial - $magvar ;
if ( $radial < 1 )
{
$radial = 360 + $radial - $magvar;
}
$radial = deg2rad($radial);
$tmp_lat = deg2rad($lat);
$tmp_lon = deg2rad($lon);
$new_lat = asin(sin($tmp_lat)* cos($range) + cos($tmp_lat) * sin($range) * cos($radial));
$new_lat = rad2deg($new_lat);
$new_lon = $tmp_lon - asin(sin($radial) * sin($range)/cos($new_lat))+ pi() % 2 * pi() - pi();
$new_lon = rad2deg($new_lon);
return $new_lat." ".$new_lon;
}
解决方案 14:
对于那些对 Java 解决方案感兴趣的人,这是我的代码:我注意到初始解决方案需要进行一些调整才能返回正确的经度值,尤其是当点位于极点之一时。有时还需要进行舍入操作,因为 0 纬度/经度的结果似乎略微偏离 0。对于较小的距离,舍入在这方面会有所帮助。
private static final double EARTH_RADIUS = 6371; // average earth radius
/**
* Returns the coordinates of the point situated at the distance specified, in
* the direction specified. Note that the value is an approximation, not an
* exact result.
*
* @param startPointLatitude
* @param startPointLongitude
* @param distanceInKm
* @param bearing: 0 means moving north, 90 moving east, 180 moving
* south, 270 moving west. Max value 360 min value 0;
* @return new point location
*/
public static LocationDTO getPointAt(double startPointLatitude, double startPointLongitude, double distanceInKm,
double bearing) {
if (Math.abs(startPointLatitude) > 90) {
throw new BadRequestException(ExceptionMessages.INVALID_LATITUDE);
} else if (Math.abs(startPointLatitude) == 90) {
startPointLatitude = 89.99999 * Math.signum(startPointLatitude); // we have to do this conversion else the formula doesnt return the correct longitude value
}
if (Math.abs(startPointLongitude) > 180) {
throw new BadRequestException(ExceptionMessages.INVALID_LONGITUDE);
}
double angularDistance = distanceInKm / EARTH_RADIUS;
bearing = deg2rad(bearing);
startPointLatitude = deg2rad(startPointLatitude);
startPointLongitude = deg2rad(startPointLongitude);
double latitude = Math.asin(Math.sin(startPointLatitude) * Math.cos(angularDistance)
+ Math.cos(startPointLatitude) * Math.sin(angularDistance) * Math.cos(bearing));
double longitude = startPointLongitude
+ Math.atan2(Math.sin(bearing) * Math.sin(angularDistance) * Math.cos(startPointLatitude),
Math.cos(angularDistance) - Math.sin(startPointLatitude) * Math.sin(latitude));
longitude = (rad2deg(longitude) + 540) % 360 - 180; // normalize longitude to be in -180 +180 interval
LocationDTO result = new LocationDTO();
result.setLatitude(roundValue(rad2deg(latitude)));
result.setLongitude(roundValue(longitude));
return result;
}
private static double roundValue(double value) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.#####");
df.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.CEILING);
return Double.valueOf(df.format(value));
}
// This function converts decimal degrees to radians
private static double deg2rad(double deg) {
return (deg * Math.PI / 180.0);
}
// This function converts radians to decimal degrees
private static double rad2deg(double rad) {
return (rad * 180.0 / Math.PI);
}
解决方案 15:
参加聚会已经很晚了,但对于任何感兴趣的人,这里有一个 R 语言的答案。我所做的唯一更改是将半径设置为米,因此d也需要设置为米。
get_point_at_distance <- function(lon, lat, d, bearing, R = 6378137) {
# lat: initial latitude, in degrees
# lon: initial longitude, in degrees
# d: target distance from initial point (in m)
# bearing: (true) heading in degrees
# R: mean radius of earth (in m)
# Returns new lat/lon coordinate {d} m from initial, in degrees
## convert to radians
lat1 <- lat * (pi/180)
lon1 <- lon * (pi/180)
a <- bearing * (pi/180)
## new position
lat2 <- asin(sin(lat1) * cos(d/R) + cos(lat1) * sin(d/R) * cos(a))
lon2 <- lon1 + atan2(
sin(a) * sin(d/R) * cos(lat1),
cos(d/R) - sin(lat1) * sin(lat2)
)
## convert back to degrees
lat2 <- lat2 * (180/pi)
lon2 <- lon2 * (180/pi)
## return
return(c(lon2, lat2))
}
lat = 52.20472
lon = 0.14056
distance = 15000
bearing = 90
get_point_at_distance(lon = lon, lat = lat, d = distance, bearing = bearing)
# [1] 0.3604322 52.2045157
扫码咨询,免费领取项目管理大礼包!







